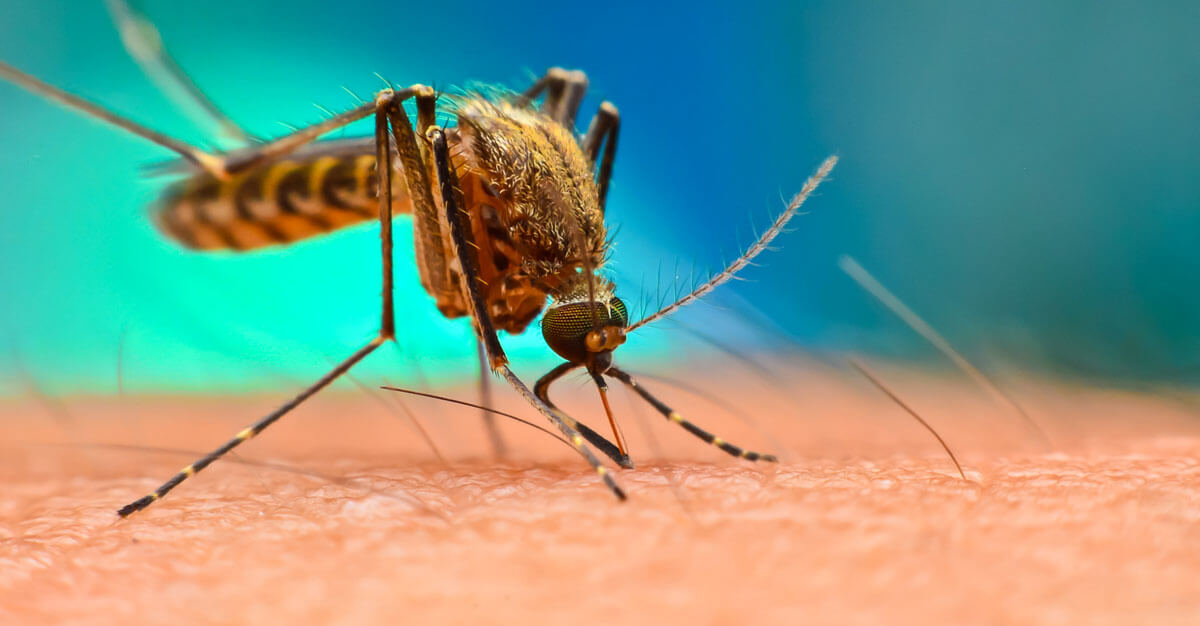
Over 7000 confirmed cases of Chikungunya virus cases have hit several parts of China’s Guangdong province since July 2025.
In Foshan City, the hardest-hit area, chikungunya patients are required to remain hospitalized, with mosquito nets placed over their beds.
They may only be discharged after testing negative or completing a mandatory seven-day stay.
Apart from Foshan City, at least 12 other cities in Guangdong Province have reported nearly 3,000 cases in the past week.
What is Chikungunya Virus?
According to the World Health Organization, chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease that causes fever and severe joint pain.
The name “chikungunya” derives from a word in the Kimakonde language of southern Tanzania, meaning “that which bends up,” and describes the stooped appearance of infected people with severe joint pain (arthralgia).
The virus is transmitted to humans by the bites of infected female mosquitoes, most commonly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes.
CHIKV was first identified in Tanzania in 1952 and subsequently in other countries in Africa and Asia.
Symptoms of chikungunya appear between 4 and 8 days (range 2–12 days) after the patient has been bitten by the infected mosquito.
Most symptoms of chikungunya are self-limiting and typically last 2–3 days. The disease begins abruptly with a high fever, often accompanied by severe joint pain.
Other common symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash. While joint pain usually resolves within days, it can persist for weeks, months, or even years in some cases.
Patients at extremes of the age spectrum are at higher risk for severe disease including newborns infected during delivery to infected mothers or bitten by infected mosquitoes in the weeks after birth, and older people with underlying medical conditions.
Patients with severe illness may require hospitalization due to the risk of organ damage and death.
However, symptoms are often mild, and infections can go unrecognized or be misdiagnosed, especially in regions where dengue and other arboviruses also occur.
Treatment is directed primarily at relieving the symptoms, including joint pain.
This is largely achieved by using anti-pyretic drugs to reduce fever, by optimizing the use of pain medication and by administering fluids.
Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should not be administered until dengue can be ruled out to reduce the risk of bleeding. There is no specific antiviral drug treatment for chikungunya.